Arabic Alphabet
Primary letters
| Stand-alone |
Initial |
Medial |
Final |
Name |
Trans. |
Value |
| ﺀ |
أ ؤ إ ئ ٵ ٶ ٸ ځ, etc. |
hamza |
ʾ / ’ |
[ʔ] |
| ﺍ |
— |
ﺎ |
ʾalif |
ā / â |
[aː] |
| ﺏ |
ﺑ |
ﺒ |
ﺐ |
bāʾ |
b |
[b] |
| ﺕ |
ﺗ |
ﺘ |
ﺖ |
tāʾ |
t |
[t] |
| ﺙ |
ﺛ |
ﺜ |
ﺚ |
ṯāʾ |
ṯ / th |
[θ] |
| ﺝ |
ﺟ |
ﺠ |
ﺞ |
ǧīm |
ǧ / j / dj |
[ʤ] |
| ﺡ |
ﺣ |
ﺤ |
ﺢ |
ḥāʾ |
ḥ |
[ħ] |
| ﺥ |
ﺧ |
ﺨ |
ﺦ |
ḫāʾ |
ḫ / ẖ / kh |
[x] |
| ﺩ |
— |
ﺪ |
dāl |
d |
[d] |
| ﺫ |
— |
ﺬ |
ḏāl |
ḏ / dh |
[ð] |
| ﺭ |
— |
ﺮ |
rāʾ |
r |
[r] |
| ﺯ |
— |
ﺰ |
zāy |
z |
[z] |
| ﺱ |
ﺳ |
ﺴ |
ﺲ |
sīn |
s |
[s] |
| ﺵ |
ﺷ |
ﺸ |
ﺶ |
šīn |
š / sh |
[ʃ] |
| ﺹ |
ﺻ |
ﺼ |
ﺺ |
ṣād |
ṣ |
[sˁ] |
| ﺽ |
ﺿ |
ﻀ |
ﺾ |
ḍād |
ḍ |
[dˁ], [ðˤ] |
| ﻁ |
ﻃ |
ﻄ |
ﻂ |
ṭāʾ |
ṭ |
[tˁ] |
| ﻅ |
ﻇ |
ﻈ |
ﻆ |
zāʾ |
ẓ |
[zˁ], [ðˁ] |
| ﻉ |
ﻋ |
ﻌ |
ﻊ |
ʿayn |
ʿ / ‘ |
[ʔˤ] |
| ﻍ |
ﻏ |
ﻐ |
ﻎ |
ġayn |
ġ / gh |
[ɣ] |
| ﻑ |
ﻓ |
ﻔ |
ﻒ |
fāʾ |
f |
[f] |
| ﻕ |
ﻗ |
ﻘ |
ﻖ |
qāf |
q / ḳ |
[q] |
| ﻙ |
ﻛ |
ﻜ |
ﻚ |
kāf |
k |
[k] |
| ﻝ |
ﻟ |
ﻠ |
ﻞ |
lām |
l |
[l] |
| ﻡ |
ﻣ |
ﻤ |
ﻢ |
mīm |
m |
[m] |
| ﻥ |
ﻧ |
ﻨ |
ﻦ |
nūn |
n |
[n] |
| ﻩ |
ﻫ |
ﻬ |
ﻪ |
hāʾ |
h |
[h] |
| ﻭ |
— |
ﻮ |
wāw |
w |
[w] |
| ﻱ |
ﻳ |
ﻴ |
ﻲ |
yāʾ |
y |
[j] |
Letters lacking an initial or medial version
are never tied to the following letter, even in a word. As to ﺀ
hamza,, it has only a single graphic, since it is never tied to
a preceding or following letter. Source:
http://ee.www.ee/transliteration/pdf/Arabic.pdf
Here is a graphic list of the Alphabet:
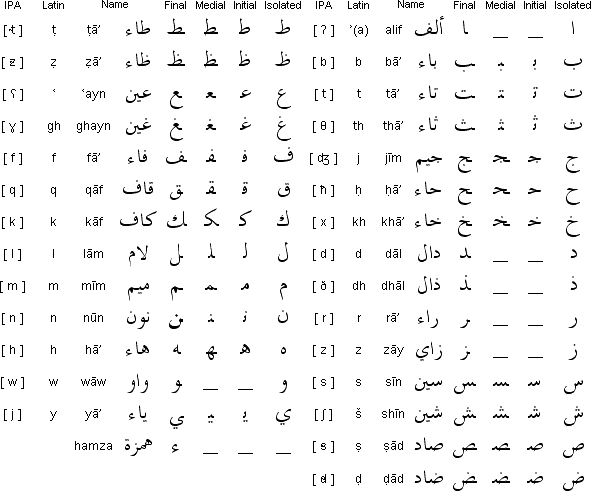
Here yet another graphic list of the
Alphabet:

Here yet another graphic list of the
Alphabet in comparison to other scripts:
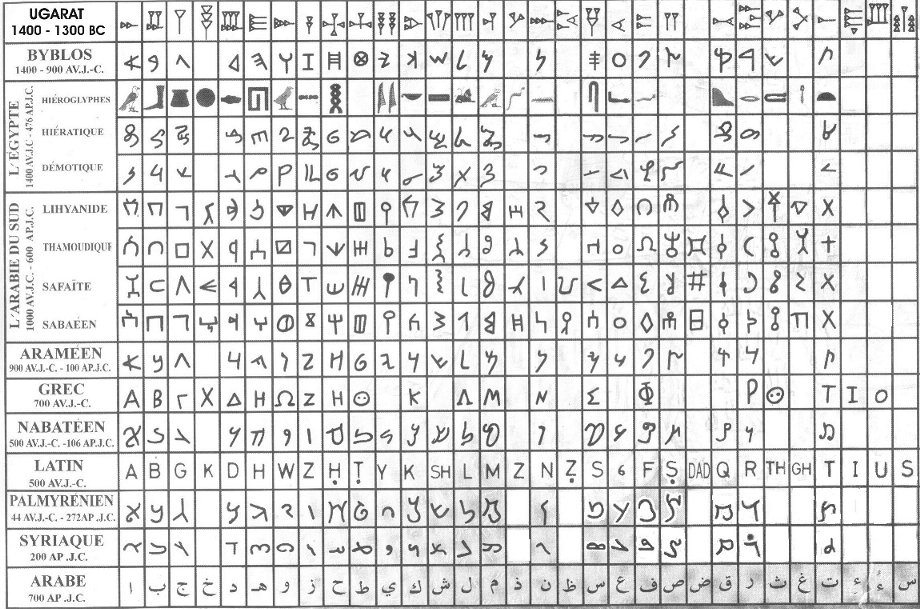
Abjad:
Abjad letter-numerals
are the letters of the Arabic alphabet given numerical values. They could thus
be used in various combinations to represent any number from 1 to 1999. It is
not a place-notational system, for their value does not depend upon their
position relative to one another. Thus the number 652 would be represented by
the letters kha',
[= 600], nun [=
50], and ba' [=
2], no matter in what order the letters were arranged. The name
abjad comes from the first
four letters in the sequence to which values 1, 2, 3, and 4 were assigned, that
is, letters, alif, ba', jim,
and dal. The
symbol for zero was derived from Greek astronomical and mathematical
manuscripts where a symbol was often used as an
abbreviation for the Greek word
ouden, meaning "nothing".
The letter-numerals for numbers 1 through 50 were the same throughout the
Islamic lands, but there were differences between the Western areas and the
Eastern when it came to assigning letters to the remaining values, as can be
seen in the following table:
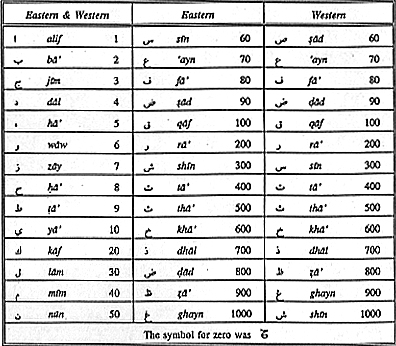
Arabic numerals

There are two kinds of numerals used in Arabic writing; standard Arabic numerals, and "EastArab" numerals, used in Arab writing in
Iran, Pakistan and India.
| Standard numerals |
| ٠ |
0 |
| ١ |
1 |
| ٢ |
2 |
| ٣ |
3 |
| ٤ |
4 |
| ٥ |
5 |
| ٦ |
6 |
| ٧ |
7 |
| ٨ |
8 |
| ٩ |
9 |
|
| EastArab numerals |
| ۰ |
0 |
| ۱ |
1 |
| ۲ |
2 |
| ۳ |
3 |
| ۴ |
4 |
| ۵ |
5 |
| ۶ |
6 |
| ۷ |
7 |
| ۸ |
8 |
| ۹ |
9 |
|
I hope these have been helpful, it
takes a while to find this stuff but its out there!




